The Rise of Smart Manufacturing in India
Introduction
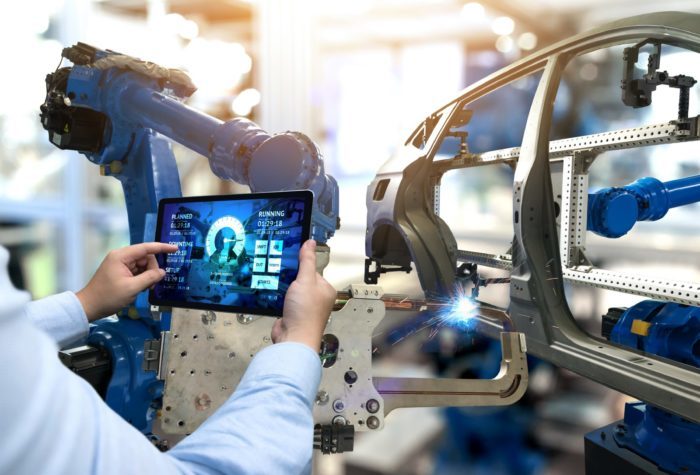
The global manufacturing landscape is undergoing a revolutionary transformation, fueled by rapid technological advancements. This wave of innovation, often referred to as Industry 4.0, is making factories smarter, more agile, and highly interconnected. At the heart of this change is smart manufacturing, which integrates digital technologies to improve productivity, enhance safety, reduce environmental impact, and drive profitability.
The question is whether Indian infrastructure is ready for this and whether it is equipped with the knowledge and skills required to adapt to these evolving advanced technology concepts
Only 28% of the Indian manufacturing industry has an implemented smart factory and across geographies, it is 43%. The wave of a smart factory started with the adoption of Industry 4.0, and since then it has been essential for the survival of the manufacturing industry. The Government’s Make in India initiative will be a key enabler of connected factories in the country is believed by Probodh Chiplunkar.
What is Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is a highly digitized and connected production environment where machines, systems, and humans collaborate seamlessly. This model relies on data-driven decision-making, real-time analytics, and adaptive technologies to optimize operations.
The Role of Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 in manufacturing represents the fusion of traditional manufacturing processes with modern technologies. It involves the integration of cyber-physical systems, AI in manufacturing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create intelligent networks along the entire product manufacturing value chain.
Key Industry 4.0 Technologies Powering Digital Manufacturing
The Industry 4.0 technologies driving the change in manufacturing industries include:
- Artificial intelligence in manufacturing
- Big Data and Analytics
- Cloud Computing
- Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Co-bots (collaborative robots)
- Sensors and Cybersecurity
- Simulation and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Virtual Reality (VR)
- Horizontal and Vertical System Integration
These manufacturing 4.0 technologies enable real-time communication between machines and people, allowing manufacturers to gather actionable insights and optimize performance.
The Status of Smart Factories in India
According to recent statistics, only 28% of Indian manufacturing industries have implemented smart factories, compared to a global average of 43%. The adoption of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing has been slow, despite the potential for increased productivity and cost savings.
The Indian government’s Make in India initiative aims to accelerate this transition by promoting innovation, encouraging foreign investments, and developing a skilled workforce.
Challenges Faced by Indian Manufacturing in Adopting Smart Technologies
1. Integration
Despite the growing interest, many India manufacturing companies struggle with integrating digital solutions. The shift toward less human supervision is seen as a barrier, especially in traditionally labor-intensive sectors.
2. Connectivity
Reliable wireless connectivity is crucial for smart systems. A modernized network infrastructure is necessary to support sensor-based tracking, real-time inventory monitoring, and quality control across supply chains.
3. Financing and Strategic Decision-Making
High costs and limited access to capital make it difficult for many businesses to adopt advanced manufacturing technology. Leadership commitment and streamlined decision-making processes are essential for strategic investments.
4. Security
As factories become more connected, cybersecurity becomes a top priority. Protecting data, communication channels, and intellectual property is crucial when adopting Industry 4.0 technologies.
5. Skills Gap
The lack of skilled professionals remains a major roadblock. Reskilling and upskilling workers to operate smart machinery and interpret data insights are necessary for a successful transition.
Benefits of Embracing Smart Manufacturing in India
Adopting smart factories and AI in manufacturing can deliver numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced asset efficiency
- Mass customization and energy efficiency
- Real-time data collection and input analysis
- Improved production resource usage
- Reduced manufacturing waste
- Increased operational safety and sustainability
- Year-on-year productivity improvements
- Better knowledge transfer and innovation cycles
Future Outlook for Digital Manufacturing in India
Machine-as-a-Service (MaaS) and M2M Connectivity
Emerging models such as Machine-as-a-Service (MaaS) are reshaping how machines are used and paid for. The Machine-to-Machine (M2M) connections are projected to reach 3.3 billion globally, supporting automation and remote control of manufacturing systems.
Robotics and Automation
By 2025, robots are expected to perform up to 25% of tasks in manufacturing worldwide, compared to just 10% today. This shift will not only improve productivity by 30% but also significantly reduce labor costs.
Role of SMEs and Startups
For a real breakthrough in smart manufacturing, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) must collaborate with IoT platform startups. These partnerships can boost efficiency, reduce costs, and accelerate technology adoption.
Conclusion
The evolution toward digital manufacturing and connected smart factories marks a pivotal moment for India’s manufacturing industries. While the path is filled with challenges—from integration to security and skill gaps—the opportunities are even greater.
To remain globally competitive, Indian manufacturers must invest in Industry 4.0 technologies, foster innovation through R&D, and develop a future-ready workforce. Early adopters will enjoy a significant competitive edge, while those slow to adapt risk becoming obsolete.
The next phase of India manufacturing will be defined by how quickly and effectively the sector embraces Industry 4.0 in manufacturing—transforming traditional factories into intelligent, adaptive, and resilient production environments.

 May 22nd, 2019
May 22nd, 2019 Exito
Exito
Leave a Reply